CLINICAL RESOURCE
A comparative in vitro study to assess the performance characteristics of several Lite Foam dressing
P.Williams, E.Bhatt, M.Walton
Advanced Medical Solutions Ltd. UK
CLINICAL RESOURCE
A comparative in vitro study to assess the performance characteristics of several Lite Foam dressings
P.Williams, E.Bhatt, M.Walton
Advanced Medical Solutions Ltd. UK
BACKGROUND
Dressing A – A new Silicone Lite Foam Border Dressing.
Dressing B – A new Silicone Lite Foam Non-Border Dressing.
Dressing C – A Lite Foam Border Dressing
Dressing D – A Lite Foam Non-Border Dressing
Dressing E – A Lite Foam Border Dressing
Dressing F – A Lite Foam Non-Border Dressing
METHOD
Breathability1 (often referred to as the MVTR or Moisture Vapour Transmission Rate) – The moisture vapour transmission across the moisture permeable backing layer is measured.
Thickness – The profile of the dressing is determined by removing the release liners of the dressing and measuring the thickness of the dressing with calibrated callipers.
RESULTS
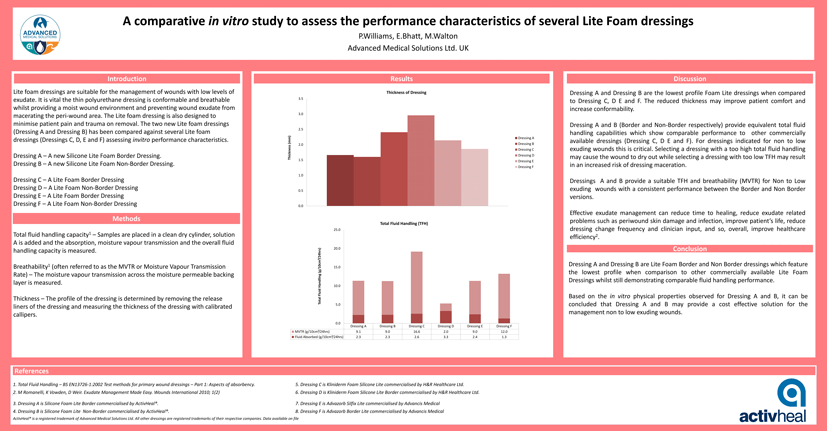
Thickness of Dressing
TOTAL FLUID HANDLING (TFH)
DISCUSSION
Dressing A and B (Border and Non-Border respectively) provide equivalent total fluid handling capabilities which show comparable performance to other commercially available dressings (Dressing C, D E and F). For dressings indicated for non to low exuding wounds this is critical. Selecting a dressing with a too high total fluid handling may cause the wound to dry out while selecting a dressing with too low TFH may result in an increased risk of dressing maceration.
Dressings A and B provide a suitable TFH and breathability (MVTR) for Non to Low exuding wounds with a consistent performance between the Border and Non Border versions.
Effective exudate management can reduce time to healing, reduce exudate related problems such as periwound skin damage and infection, improve patient’s life, reduce dressing change frequency and clinician input, and so, overall, improve healthcare efficiency2.
CONCLUSION
Based on the in vitro physical properties observed for Dressing A and B, it can be concluded that Dressing A and B may provide a cost effective solution for the management non to low exuding wounds.
References
- Total Fluid Handling – BS EN13726-1:2002 Test methods for primary wound dressings – Part 1: Aspects of absorbency.
- M Romanelli, K Vowden, D Weir. Exudate Management Made Easy. Wounds International 2010; 1(2)
- Dressing A is Silicone Foam Lite Border commercialised by ActivHeal®
- Dressing B is Silicone Foam Lite Non-Border commercialised by ActivHeal®
- Dressing C is Kliniderm Foam Silicone Lite commercialised by H&R Healthcare Ltd.
- Dressing D is Kliniderm Foam Silicone Lite Border commercialised by H&R Healthcare Ltd.
- Dressing E is Advazorb Silfix Lite commercialised by Advancis Medical
- Dressing F is Advazorb Border Lite commercialised by Advancis Medical
ActivHeal® is a registered trademark of Advanced Medical Solutions Ltd. All other dressings are registered trademarks of their respective companies. Data available on file
CONTACT US FOR MORE INFORMATION
DISCOVER ACTIVHEAL®

OUR PRODUCT RANGE
AMS GROUP

TRAINING & EDUCATION
Discover ActivHeal®
Our Product Range
AMS Group
Training & Education

ActivHeal is a registered trademark of Advanced Medical Solutions Ltd. Only applicable in the EU.
ActivHeal is a registered trademark of Advanced Medical Solutions Ltd. Only applicable in the EU.
>> Site Map